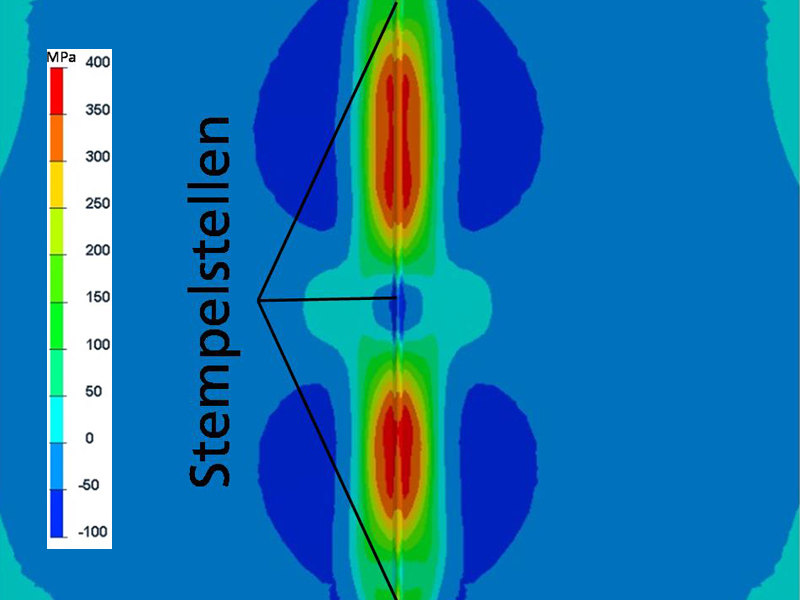
The heterogeneous nature of welding in which the material is heated up locally and cools down induces internal stresses and leads to component distortion. This has a negative effect on component quality and functionality and can also cause damage, e.g cracks, and/or reduce the service life. Internal stress and distortion are closely related, and many factors lead to their generation. The material properties, clamping conditions as well as welding procedure and parameters all play an important role. Numerical welding simulation can be used to identify the optimal clamping conditions and welding parameters that minimize the distortion and residual stresses.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Mechanics of Materials IWM
Fraunhofer Institute for Mechanics of Materials IWM